Introduction
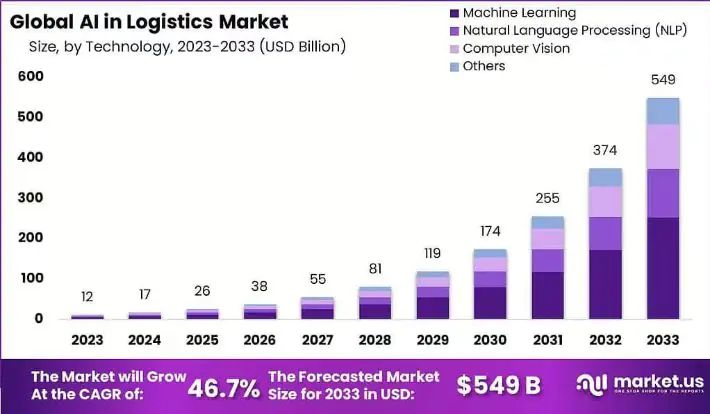
From USD 12 billion to USD 549 billion in a decade, there has been mammoth growth for AI in the logistics and supply chain industry globally. A CAGR of 46.7 percent supports the stunning projection. The logistics sector worldwide has been seeking technological transformation for a long time. Logistics software development companies are turning to AI technology to solve efficiency, cost, growth, and customer satisfaction-related woes.
Image Courtesy: market.us
Current challenges recognized in logistics and supply chain management are increased demand variability, transportation issues, and inventory issues, all this while attempting to satisfy higher levels of customer demand.
AI in supply chain management is, hence, revolutionizing logistics & supply chain management by raising productivity, reducing human error, and improving data analysis.
In this post, we will provide details of certain AI logistics solutions, their advantages, difficulties in implementation, and trends that define their future.
Understanding Logistics and Supply Chain Operations
Definition and Importance
Logistics vs. Supply Chain:
Logistics is concerned with the flow of goods within a supply chain network. Transportation, storage, and the record of the keeping of stocks are all in one basket.
Supply chain management is more extensive because SCM is responsible for managing the total flow of material and finished products from their origin to the consumer. Logistics is one of the components.
Economic Impact:
Supply chain optimization results in a general enhancement of business outcomes due to decreased expenses and provides greater suitabilities to market requirements.
Investing in logistics app development can greatly enhance organizations’ overall cash inflow, provide higher levels of customer satisfaction, and spearhead a more decisive competitive edge in the market.
Current Challenges in Logistics and Supply Chain
Common Issues:
Some of the most crucial issues are demand forecasting, inventory management with AI, transportation planning, and having an overall view, mostly in multinational and distributed environments.
Impact of Inefficiencies:
These challenges escalate operating costs, delay delivery of goods and services, and leave unsatisfied customers, which translates to loss-making positions and positions in the market for any company.
How AI is Revolutionizing Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Artificial intelligence in logistics is viewed as an evolutionary fulcrum for the industry. North America leads the AI-based technological innovation in the supply chain industry. From managing stocks in the warehouses to forecasting consumer demand and from automation in operations to predictive analytics in logistics decision-making, AI in logistics is elevating logistics businesses to newer heights in growth momentum as well as in customer satisfaction.
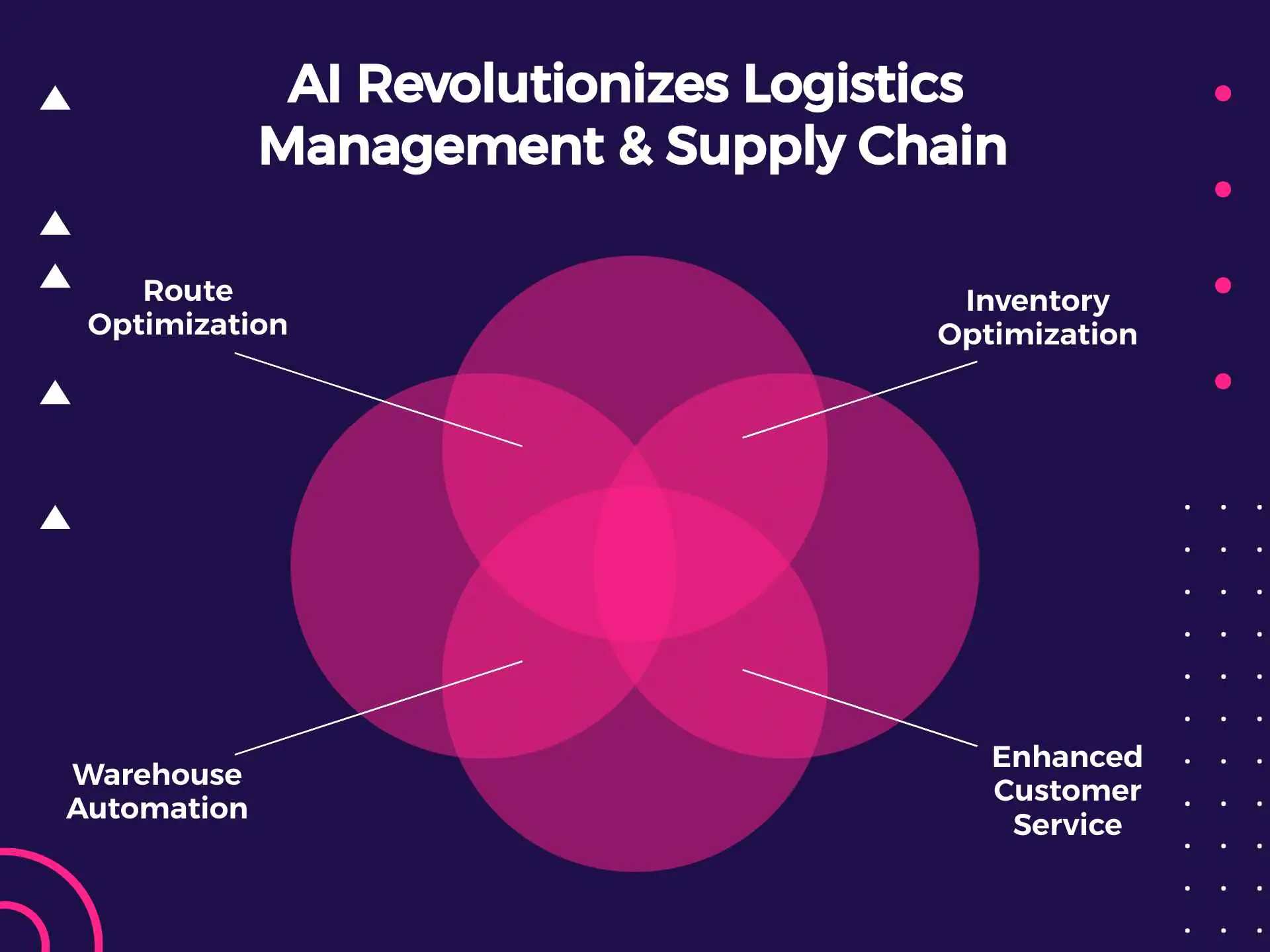
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
Predictive Analytics:
AI technologies use past records, current market data, and external factors in order to enhance the rate of demand forecasting and subsequently avoid stockouts while optimizing inventory.
Dynamic Inventory Management:
There is a constant adjusting of supply to the needs of customers through automatic replenishment systems, which cuts stock costs from overstocking and out-of-stock situations.
Route Optimization and Transportation Management
Real-Time Data Analysis:
AI integrates traffic, weather, and delivery data to define the most suitable routes, making delivery much faster and enhancing overall transportation.
Cost Reduction:
As stated earlier, these efficient routes minimize fuel consumption, vehicle depreciation, and overtime costs while at the same time enhancing on-time delivery performance.
Warehouse Automation and Robotics
Automated Systems:
To transform warehouse management, AI in the supply chain offers intelligent sorting systems, like Arduino, AMR, as well as AI-based picking strategies to improve productivity.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
The automation of repetitive tasks is one of the benefits of RPA since it increases orders’ processing accuracy. Comparative advantages of using robotic process automation (RPA) include cost reduction since resources are not wasted on repetitive tasks.
Enhanced Customer Service and Experience
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Self-service through an order-tracking chatbot saves customers time and increases satisfaction levels. It also applies customer service automation to answer multiple questions about shipping, etc.
Personalized Communication:
AI supply chain solutions cater communication to customers by evaluating their information to anticipate their behavior, for instance, a record of individually customized selling indicators.
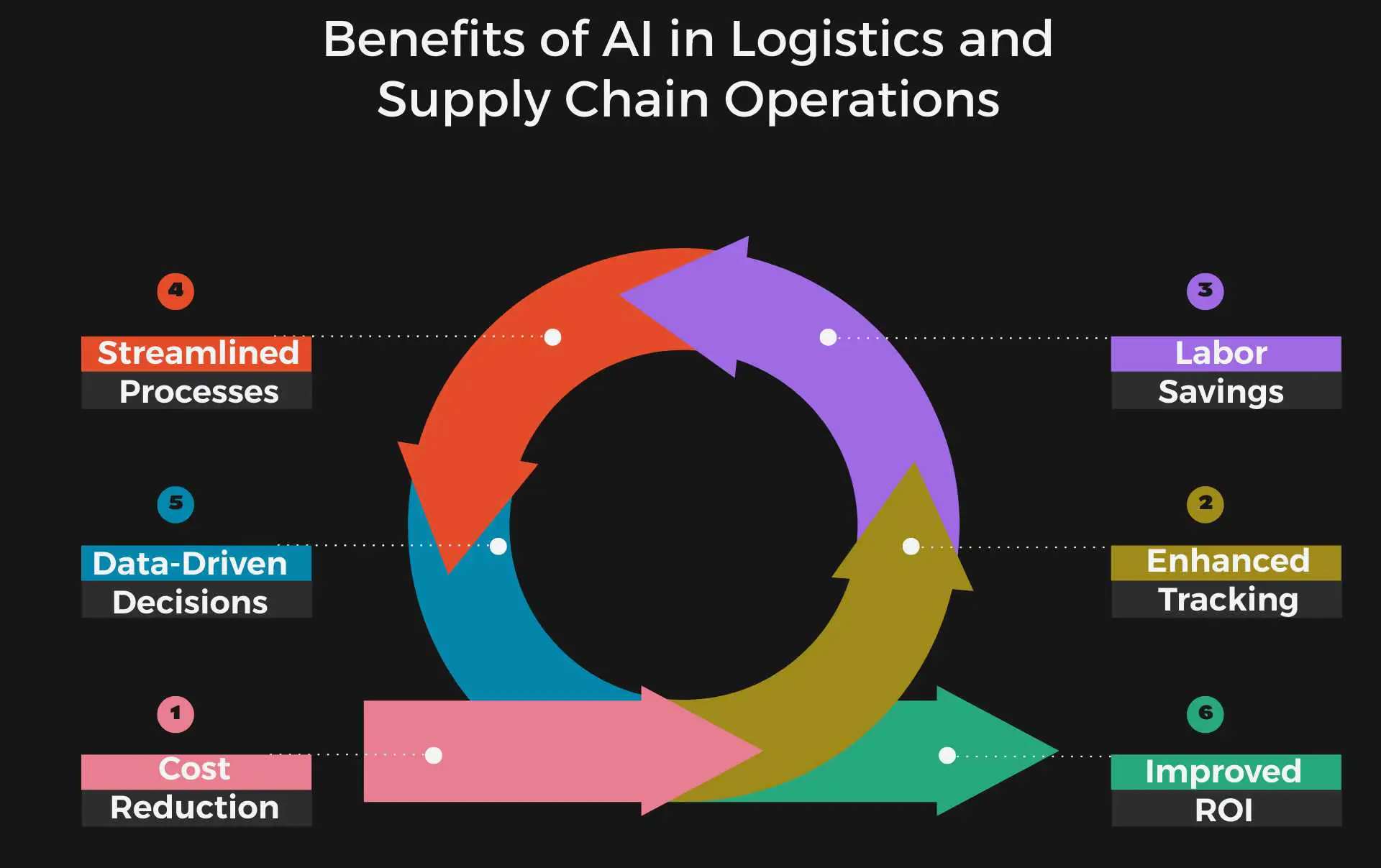
Benefits of AI in Logistics and Supply Chain Operations
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Streamlined Processes:
AI makes operations leaner from time loss caused by bottlenecks resulting from maintaining routine processes like data processing and analysis that slow down operations in logistics.
Labor Savings:
Outsourcing relieves time for the execution of simple activities, thus allowing human capital such as planning, cost management, customer relations, and problem-solving, thus enhancing productivity.
Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Data-Driven Decision Making:
The use of AI helps in cutting down the possible mistakes in the analysis of data requirements about inventory, identification, and the subsequent path.
Enhanced Tracking and Monitoring:
AI tools enhance the supply chain management process because real-time tracking of consignments and identification, as well as solving various issues, only takes place in real-time.
Cost Savings and Profitability
Operational Cost Reduction:
AI offers opportunities for reducing the cost of managing inventories, cutting costs on transportation, and deploying resources for logistic activities.
Return on Investment (ROI):
Implementing an AI logistics system has many advantages that any business is likely to receive in exchange for their investment after some time, including a lower number of mistakes and a high level of satisfaction among clients.
Case Studies: Successful AI Implementations in Logistics
Amazon
Innovative Strategies:
Some of the creative ways that Amazon has embraced the use of AI in the supply chain include use in demand planning, warehouse automation, and last-mile delivery.
DHL
Smart Logistics:
Several examples include its use in establishing the most reliable avenues in the case of transport, offering anticipations on when such transports are likely to be in need of some maintenance, and the use of robots in sorting out the items as a way of improving the general logistics within DHL.
Walmart
Inventory Management:
Currently, artificial intelligence is employed in Walmart in order to improve effectiveness in stocking its large chain of stores through applications in inventory management, demand planning, and supply chain.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Logistics
Data Quality and Availability
Challenges with Data:
AI is highly suited to function in high-quality and easily processed ‘data’ inputs. Several organizations face problems in the sectioning of data and variations in procedures used in data collection.
Resistance to Change
Cultural Barriers:
Last but not least, social resistance in the organization is one of the biggest factors that has led to the slow adoption of AI technologies in organizations. There is a need to change control and employee training in an organization to increase its profitability.
Cost of Implementation
Initial Investment:
One of the key factors that have been realized to pose a challenge to organizations is the implementation of AI in logistics, which entails the use of capital in technology, equipment, and people.
Machine Learning and Supply Chain Regulation: The Future Trends
Larger application of Machine Learning
Evolution of Algorithms:
It will grow the application of AI machine learning in enhancing predictive analysis and develop better ways of integrating theory for better utilization among logisticians and supply chain managers.
Integration with IoT
Smart Supply Chains:
The integration of AI and IoT will give birth to intelligent supply chains of the future, where the real status of connected devices is feeding AI systems.
Sustainable Practices
AI for Sustainability:
AI, which is the key aspect of Tetley’s plan, will help in the effective management of logistics for sustainability and lower carbon emissions through effective routing, load, and energy management.
Conclusion
AI in logistics and supply chain management has been observed to make the work more efficient, accurate, and faster in making decisions affecting work involving inventory management, transportation of goods, and relations with customers.
Discover how AI in the logistics sector enhances supply chain operations and increases your performance in the modern business world.
If you want to know how to optimize route optimization with AI, get in touch with our consultancy service to book an individual consultation.
FAQs
AI wears multiple hats when it comes to the logistics sector. However, AI’s most impactful role in improving customer satisfaction is taking over repetitive tasks, including route optimization, which results in improved visibility for customers and cost reduction for freight brokers.
AI takes on business performance and improves it many folds by automating repetitive tasks, managing inventory, improving visibility, predicting demands, and reducing operations costs.
Issues of concern are quality, change management, costs of implementing AI, and compatibility of the solution with existing systems.
AI in logistics will advance in machine learning, IoT interconnectivity for smart supply chains, and the adoption of sustainable ideas.